Key Takeaways
- XCI files function as complete cartridge copies that include the full game, metadata, and sometimes updates. They’re easy to load but take up more storage space.
- NSP files serve as digital installers used for base games, updates, and DLCs. They’re lightweight and flexible, making them ideal for emulator setups.
- NCA files hold the core data of a game, such as code, textures, and audio files. They work behind the scenes inside XCI and NSP packages.
- Each format has its own role: XCI for full dumps, NSP for digital installs, and NCA for internal data. Understanding them ensures smooth game management.
- Picking the right file format improves performance, reduces errors, and helps organize your Nintendo Switch library more efficiently.
Nintendo Switch game files mainly come in XCI, NSP, and NCA formats, each designed for specific uses. XCI files mirror physical cartridges and offer complete game dumps, while NSP files handle digital installations, updates, and DLCs more efficiently. NCA files store the core game data like code, textures, and audio. Understanding these formats helps organize, install, and manage games smoothly on both consoles and emulators like Yuzu and Ryujinx.
What Are Nintendo Switch Game Formats?
Nintendo Switch games come in three main file formats: XCI, NSP, and NCA. Each one serves a unique purpose, whether you’re playing from a cartridge, downloading from the eShop, or using an emulator like Yuzu or Ryujinx.
Understanding these file types helps gamers manage their libraries better, avoid errors, and improve performance. In 2025, as more players switch to digital and emulation platforms, knowing these formats is more important than ever.

Why Understanding Game Formats Matters in 2025?
The Nintendo Switch ecosystem is evolving, and so are its game formats. Many players now back up their games digitally or use emulators for convenience. Knowing which file format does what can:
- Prevent compatibility issues with Yuzu or Ryujinx.
- Save storage space by using the right file type.
- Ensure smooth updates and better performance.
As digital gaming becomes the norm, having clarity about these files can make your gaming experience easier and safer.
Overview of Nintendo Switch File Formats
Switch game files are stored in several structures depending on how they were obtained or installed. Let’s break down the key formats and what each means.
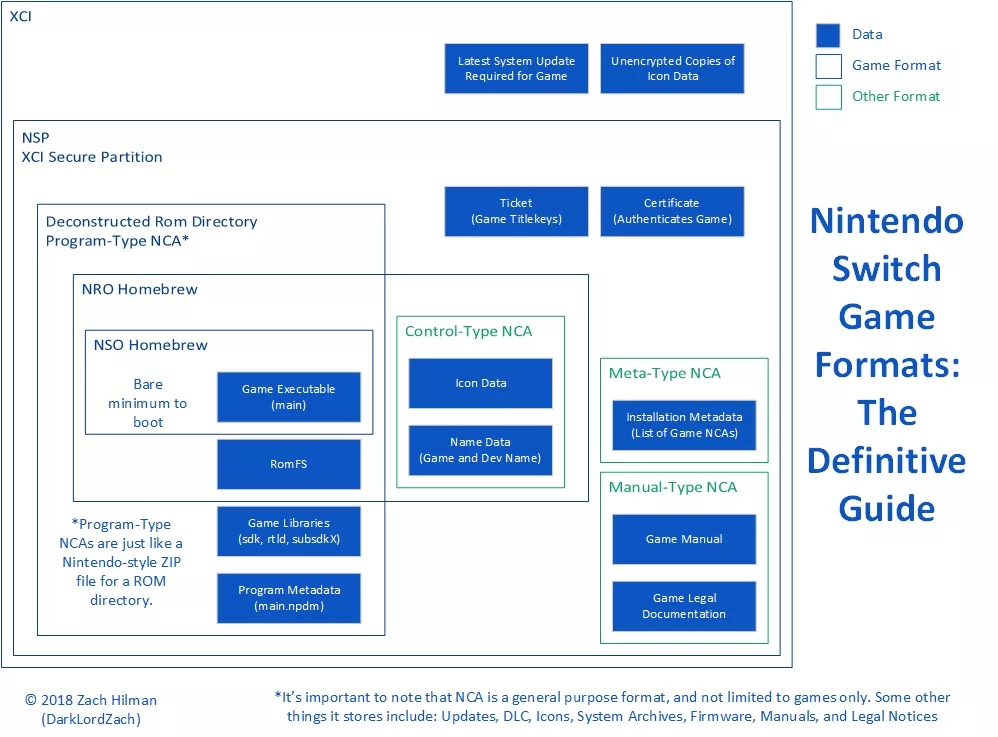
1. XCI Format (Game Card Dumps):
An XCI file is a complete dump of a physical Nintendo Switch cartridge. It contains everything that’s on the original game card including the base game, icon, metadata, and in some cases, updates or patches. Essentially, it replicates the exact structure of a real cartridge, making it a preferred format for those who want a faithful digital backup of their games.

Used For:
- Backing up physical game cartridges: XCI files are commonly used to create a secure digital copy of your owned game cards.
- Playing games offline via emulators like Yuzu or Ryujinx: Since they contain everything needed to run the game, they’re ideal for offline use without connecting to Nintendo’s servers.
- Preserving original cartridges: XCI dumps serve as archival copies, ensuring your physical games remain protected even if the original cartridge gets damaged or lost.
Pros
Cons
Personal Note:
When I first tried using an XCI file on Yuzu, it amazed me how quickly the game loaded compared to NSP. It truly felt like inserting a real cartridge. But as my collection grew, managing storage became difficult, which led me to explore lighter formats.
2. NSP Format (Digital Game Packages):
An NSP file is a complete digital package used for installing and playing Nintendo Switch games. It mirrors how the Nintendo eShop delivers games, making it ideal for digital collectors and emulator users. Unlike XCI files that represent cartridges, NSP files represent eShop-style installations: compact, installable, and easy to update.

Used For:
- Digital game installation: NSP files are used to download and install games digitally, just like titles purchased from the Nintendo eShop.
- Game updates and DLCs: They store and install updates, patches, and downloadable content, helping players expand or improve their games easily.
- System and NAND backups: NSP files are used to back up digital games or NAND data, ensuring your purchases and saves remain safe.
- Emulator installation: They allow smooth installation and gameplay on emulators like Yuzu and Ryujinx without needing physical cartridges.
Pros
Cons
Personal Experience:
When I switched from XCI to NSP files, I noticed the loading felt smoother and managing updates became much easier. For players using Yuzu, NSPs offer better flexibility, especially when testing new versions, patches, or DLCs without reinstalling the entire game.
3. NCA Format (Nintendo Content Archive)
An NCA file is one of the core components of Nintendo Switch software. It contains compressed data such as game code, audio, textures, and system resources. You can think of it as a container that holds all the essential files a game or update needs to run. NCA files are not directly playable but are crucial for developers and modders who study or modify game content.

Used For:
- Game data storage: NCA files store the main elements of a game, including executable code, textures, and sound files that make up the entire program.
- System archives and updates: They are used in official firmware and system updates to manage core console features and background processes.
- Development and modding: Developers and modders use NCA files to extract, analyze, or edit data for custom patches, mods, or learning purposes.
Pros
Cons
Developer Insight:
Advanced users often deconstruct NCA files to explore a game’s structure, tweak textures, or develop mods and patches. It’s a powerful format that plays a key role in the development and customization side of Nintendo Switch software.
Other Switch File Types You Should Know
The Nintendo Switch uses several different file types besides XCI, NSP, and NCA. These include formats for homebrew apps, game saves, and system data. Knowing about them helps you understand how the Switch works and how different files serve unique purposes.
NSO and NRO (Homebrew Applications)
NSO and NRO files are used for homebrew applications: community-made software designed to run on the Nintendo Switch outside of official Nintendo channels. These files allow developers and enthusiasts to create custom tools, emulators, utilities, or even fan-made games. While they open up exciting creative possibilities, they also require caution, as unofficial content can sometimes pose security risks if not sourced carefully.
Used For:
- Custom emulators and tools: These files are used to create and run emulators, media players, and debugging utilities, allowing users to experience non-official software on their Switch or emulator.
- Unofficial community-made apps: They enable fan-developed games, mods, and homebrew experiments, expanding the console’s capabilities beyond Nintendo’s standard limits.
- Testing and development: Developers often use NSO and NRO formats to prototype, test, or debug their own creations before making them public.
Pros
Cons
Note:
While exploring homebrew applications can be exciting and educational, it’s important to only download NSO and NRO files from trusted, verified sources. Many unsafe versions online can contain malware, corrupted files, or system-breaking code, so always prioritize security and reliability when experimenting with homebrew content.
Deconstructed ROM Directory
A Deconstructed ROM Directory is an expanded form of an NCA file, where every game asset such as code, textures, sounds, and models is unpacked and stored separately. It gives developers full access to a game’s inner structure, making it useful for testing and studying performance.
Used For:
- Debugging and modification: It is used by developers and modders to fix bugs, adjust graphics, or change in-game features without repacking the full game file.
- Deep-level analysis: It is used to explore and understand how different assets and systems within a game interact, helping in performance tuning and design improvements.
This format isn’t common for regular players but is highly valuable for developers, modders, and researchers who want to understand how Nintendo Switch games function internally.
Comparison: XCI vs NSP vs NCA
Understanding the difference between these formats helps you choose what’s best for your needs.
Format | Purpose | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
XCI | Cartridge dump | Physical game backups | Full package, easy to load | Large size |
NSP | Digital install | eShop games & updates | Manageable, flexible | Needs firmware |
NCA | Game data archive | Developers & modders | Compact, detailed | Not playable |
Use XCI for physical game backups, NSP for digital games and updates, and NCA for system-level or modding purposes.
Common Errors and How to Fix Them
While using Nintendo Switch emulators like Yuzu or Ryujinx, it’s common to encounter errors related to file formats such as XCI, NSP, or NCA. These usually happen when a game file is corrupted, outdated, or not properly configured with the right keys and firmware. Here’s a more detailed look at common issues and how to fix them:
File type not supported
Update Yuzu or Ryujinx to the latest version to ensure compatibility with newer file formats and encryption methods.
Missing keys
Make sure the correct prod.keys and title.keys files are placed in the emulator’s “keys” folder. Also, ensure your firmware matches the version required by the game.
Game failed to load
Re-verify the file’s integrity or redump the game using a trusted tool. You can also try re-importing the file into your emulator after verifying its size and checksum.
Future of Switch Game Formats (2025 and Beyond)
Nintendo is moving toward a cloud-first future. As cloud gaming expands, the reliance on traditional formats like XCI and NSP may decrease.
However, for offline gamers and preservationists, these file types will remain essential for maintaining access to classic titles. Emulators like Yuzu continue improving their support for new firmware, ensuring these formats stay relevant for years to come.
Conclusion
In 2025, understanding Nintendo Switch file formats is essential for every gamer who wants to manage and enjoy their games efficiently. Knowing how each format works makes it easier to organize files, fix errors, and keep everything running smoothly on both real consoles and emulators. It helps you make smarter choices about storage, performance, and preservation.
As technology keeps advancing, staying updated and using safe, verified game files is more important than ever. Always rely on official dumps, keep your emulators current, and play responsibly. With the right knowledge, you can enjoy a smoother, safer, and more reliable Nintendo Switch gaming experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. Can I convert NSP files to XCI format?
Yes, you can convert NSP files to XCI using trusted conversion tools. This process repackages the digital install files into a single cartridge-style format that’s easier to load in emulators. Just make sure your firmware and tool versions are compatible to avoid corrupted files.
Q 2. What’s the performance difference between XCI and NSP in Yuzu?
In Yuzu, both XCI and NSP perform similarly once installed, but NSP files usually install faster and take up less space. XCI files, on the other hand, run instantly like cartridges but require more storage and longer transfer times.
Q 3. Why do Switch games have multiple NCA files?
Switch games often include several NCA files because each file holds a different type of game data, such as code, audio, or textures. This modular design allows Nintendo to issue smaller updates, replacing only the NCAs that have changed instead of the whole game.
Q 4. Can Yuzu automatically apply NSP updates?
Yes, Yuzu automatically detects update NSPs when installed alongside the base game. If the update’s title ID and region match the main file, Yuzu merges them seamlessly, showing the latest version during launch without manual setup.
Q 5. How can I check the version of an XCI or NSP file?
To check the version of a Switch game file, open Yuzu or Ryujinx and right-click the title to view its properties. The version, title ID, and region appear there. Many NSP and XCI files also display version details in their filenames or internal metadata.