Key Takeaways
- Nintendo Switch emulators evolved rapidly from 2017 onward, transforming simple research projects into high-performance gaming platforms.
- Yuzu and Ryujinx became the leading emulators, setting new standards for speed, graphics quality, and community collaboration.
- Open-source contributions played a major role, helping developers fix bugs, improve FPS, and add modern features like 4K resolution and multiplayer support.
- Continuous innovation made Switch games playable on PCs, laptops, and handheld devices such as the Steam Deck.
- The global gaming community’s passion and teamwork turned emulation into a powerful example of technical creativity and preservation.
- Today, Nintendo Switch emulation represents how far technology and fan dedication can go in enhancing and preserving gaming experiences.
Nintendo Switch emulators have grown from simple experiments into powerful tools that recreate the console’s experience on PCs and handheld devices. Through years of community effort and open-source innovation, performance, graphics, and compatibility have improved dramatically. Today, they stand as a testament to how technology and passion can keep gaming experiences alive across generations.
Rise of the Nintendo Switch and the Birth of Emulation:
When Nintendo released the Nintendo Switch on March 3, 2017, it revolutionized gaming by combining portability and home-console power. Its hybrid design, detachable Joy-Con controllers, and vibrant exclusives such as The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild made it an instant hit.
Selling over 146 million units worldwide, the Switch became one of the best-selling consoles in history. As its popularity soared, tech enthusiasts and open-source developers grew curious about how it worked, leading to the first steps toward emulation.
Emulation, in simple terms, means recreating a console’s hardware and software environment on another platform: like running Switch games on a PC or Steam Deck. It became both a technical challenge and a passion project for gamers eager to explore the console’s inner workings.
2017 – The Early Research Phase:
In 2017, as the Switch’s architecture became public, developers began studying its operating system, Horizon. Built on a microkernel inspired by FreeBSD, it powered the console’s unique combination of portability and performance.
Community programmers began reverse-engineering Horizon and the NVIDIA Tegra processor to understand how the console handled game rendering and hardware communication. This year laid the groundwork for the first functional emulators, establishing the foundation for the years ahead.
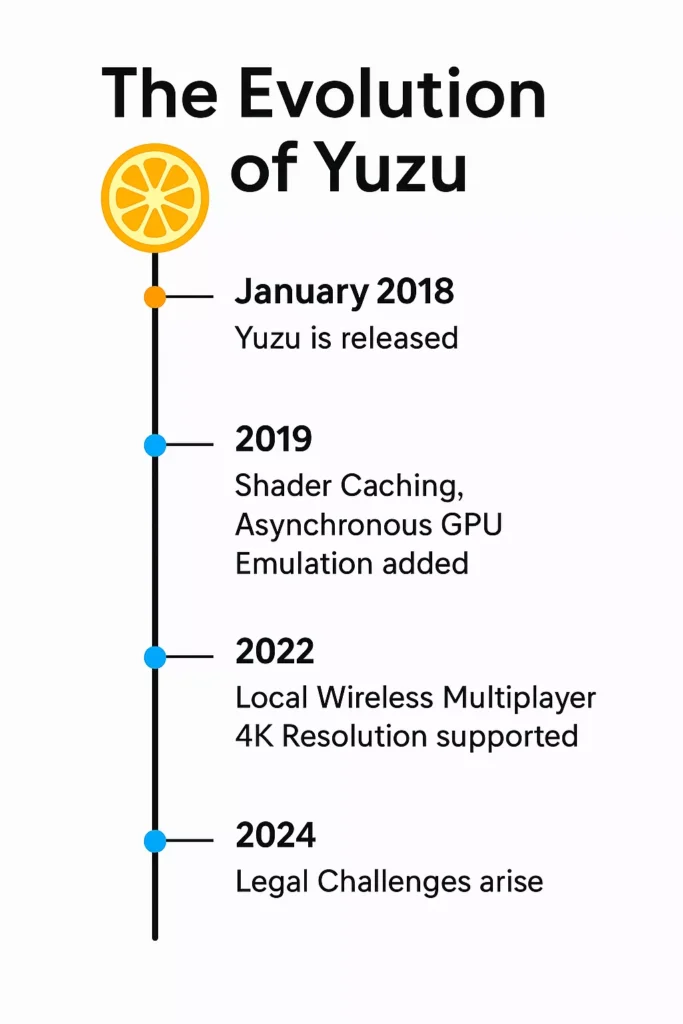
2018 – Breaking Ground with Yuzu and Ryujinx:
By early 2018, two major emulation projects emerged: Yuzu and Ryujinx.
Yuzu, created by the same developers who made the famous Citra emulator for Nintendo 3DS, became the first Nintendo Switch emulator capable of booting games. Initially, it struggled with crashes, missing textures, and heavy performance issues, but it was a crucial breakthrough.
Later that year, Ryujinx entered the scene. Written in C#, Ryujinx aimed for stability and compatibility rather than speed. It quickly gained popularity for its user-friendly interface and steady performance.
Though both emulators were in their infancy, they marked the beginning of real Switch emulation sparking excitement across Reddit, GitHub, and emulator forums.
2019 – 2020 – Rapid Progress and Feature Expansion:
Between 2019 and 2020, emulator technology advanced at lightning speed. Both Yuzu and Ryujinx introduced major performance improvements:
- Shader caching reduced stutter and load times.
- Asynchronous GPU emulation increased frame rates.
- Multicore CPU optimizations improved compatibility with more titles.
Games like Super Mario Odyssey and Pokémon Let’s Go! became fully playable for the first time, with smoother visuals and more consistent FPS.
As both emulators were open-source, they often shared innovations. Developers from around the world contributed bug fixes, feature requests, and new rendering techniques. This collaboration gave rise to one of the most active open-source gaming communities in history.
2021 – Growing Popularity and Player Support:
By 2021, Nintendo Switch emulation had entered mainstream gaming culture. Streamers and YouTubers showcased gameplay comparisons between real consoles and emulator builds, drawing millions of views.
Yuzu introduced telemetry, automatically collecting crash data to help developers identify bugs faster. This feature alone significantly improved stability and compatibility.
Users could now enjoy:
- Resolution scaling up to 1080p or higher.
- Custom texture packs and mods unavailable on the original console.
- Better controller mapping and easier UI navigation.
The gaming community’s collaborative spirit helped refine both Yuzu and Ryujinx into powerful tools capable of delivering near-console-quality experiences.
2022 – 2023 – Multiplayer, Portability, and Next-Gen Features:
From 2022 onward, Switch emulators became smarter and more feature-rich.
- Local wireless multiplayer was added, allowing friends to connect over LAN or Wi-Fi.
- Compatibility expanded to include Steam Deck and Linux-based devices, giving players portable emulation freedom.
- Support for 4K resolution and post-processing filters made Switch titles look better than ever before.
Players could now experience games like Mario Kart 8 Deluxe and Animal Crossing: New Horizons in ultra-HD with buttery-smooth performance.
This era cemented Yuzu and Ryujinx as symbols of innovation in open-source gaming.
2024 – The Turning Point and Community Transition:
By 2024, the landscape of Switch emulation began to change. Major development slowed, and new community projects emerged as enthusiasts experimented with performance, UI, and optimization.
These forks continued to push the boundaries of emulation technology, keeping the spirit of innovation alive. Developers focused more on performance testing, cross-platform support, and preserving old builds for future research.
Even as mainline projects evolved, the global gaming community remained passionate about maintaining and improving emulator accessibility.
What is the Role of the Community in Emulator Growth?
The evolution of Nintendo Switch emulators wouldn’t have been possible without its community. Thousands of testers, coders, and gamers joined forces to share bug reports, compatibility lists, and performance tweaks.
Open-source collaboration turned small side projects into global movements. Discord and Reddit communities provided step-by-step guides, while YouTubers demonstrated gameplay optimization for different PC setups.
This collective passion showcased how gaming communities can create, innovate, and preserve technology together.
What is the Future of Nintendo Switch Emulation?
The next phase of Nintendo Switch emulation looks promising. As new technologies like AI upscaling, DLSS enhancements, and multi-threaded rendering evolve, emulators will continue to become more efficient and realistic.
Developers are already experimenting with machine learning to optimize graphics, while community contributors work on next-gen compatibility for upcoming Nintendo systems.
With dedication and teamwork, emulation will remain an essential tool for game preservation and technical innovation, ensuring classic titles never fade away.
Conclusion
The journey of Nintendo Switch emulators reflects the creativity and determination of the gaming world. From early research in 2017 to advanced, high-performance builds in 2024, each milestone represents years of dedication, collaboration, and innovation.
These emulators not only extended the life of Switch games but also inspired new generations of developers to explore the intersection of software engineering and gaming.
As the community continues to grow, one truth remains clear, emulation is more than just technology; it’s a tribute to the love of gaming, the art of preservation, and the endless pursuit of improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. Which Nintendo Switch emulator runs the most games smoothly?
Among past emulators, Ryujinx was widely praised for its stability and consistent frame rates, while Yuzu was known for advanced features and customization. The performance often depended on a user’s hardware setup, high-end CPUs and GPUs delivered smoother gameplay.
Q 2. Can Nintendo Switch emulators work on Android phones or tablets?
Most Nintendo Switch emulators were designed for Windows, Linux, and macOS platforms. However, several experimental Android ports appeared later, with limited success due to hardware constraints. Mobile versions often struggle with demanding titles that require high-end GPUs.
Q 3. How do emulator updates improve game performance over time?
Each emulator update introduces optimized rendering, better shader caching, and reduced CPU overhead, allowing games to load faster and run more efficiently. Frequent updates also fix bugs, expand game compatibility, and improve controller response for a smoother experience.
Q 4. What are the system requirements to run Nintendo Switch emulators on PC?
While requirements vary by emulator, most recommend at least:
CPU: Quad-core (Intel i5/Ryzen 5 or higher)
GPU: NVIDIA GTX 1060 / AMD RX 580 or better
RAM: 8–16 GB
Storage: SSD for faster game loading
These specs ensure high performance and stable frame rates for demanding Switch games.
Q 5. Will emulation continue to evolve with next-generation Nintendo consoles?
Yes. As technology advances, emulator developers are expected to adopt AI-driven rendering, multi-threaded optimizations, and next-gen hardware compatibility. Future emulators may support hybrid systems similar to the Switch, ensuring long-term preservation and playability of upcoming titles.


